WHY BECOME A NURSE PRACTITIONER?
Becoming a nurse practitioner (NP) can widen career prospects and improve salary potential. Through your studies, you may gain expertise as well as the skill to lead and collaborate.
OPPORTUNITY
NPs may conduct research, teach staff, or provide consultation services. Many choose to work with certain groups such as adult and geriatric health, or psychiatric and mental health.
SALARY
Also, as an NP, you may see a decent boost in salary. Just to give you an idea of potential earnings, in 2023 the average annual salary for APRNs was $129,480. This was higher than the average annual salaries for RNs which was $86,070. That’s $44,680 higher.
AUTONOMY
It can also bring more autonomy in a medical setting and the freedom to choose a nursing niche. One example is Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP). FNPs often work in a cooperative practice with physicians and other providers. Becoming an FNP means you may fulfill a complementary role to the traditional medical care doctors provide.
Are nurse practitioners doctors? No, but NPs may diagnose and treat illness as part of a health team or on their own. Many promote wellness and disease prevention. Like doctors, they can order, perform or assess lab work, x rays and more. Some NPs also prescribe medication. In other words, NPs take a more active role in patient care than RNs.
What credentials are needed for a nurse practitioner? A Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) is the entry degree rule to become an NP. It is also the most common degree program in the field. Though some experts note that in the future all NPs may have to earn a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) degree. Apart from the degree, you’ll need to pass a national certification exam to earn a second license.
ARE NURSE PRACTITIONERS IN HIGH DEMAND?
On the practical side, now is a great time to become a nurse practitioner. You’ll be building some in demand skills. Because of an aging population, changes in health care and other factors, there’s a huge need for APRNs. In fact, overall employment growth for NPs and FNPs is 40%. That’s much faster than average.
Online NP Program Specialization | Program Description | Prerequisite Degree |
MSN – Family Nurse Practitioner Primary Care Population | Study primary care for the management of acute and chronic health problems of both adult and pediatric patients | BSN/RN license |
Adult Gerontology Primary Care Nurse Practitioner (AGNP)Certificate program | Primary care AGNPs focus their practice on clients 13 years of age and older. Students in this program will be proficient in care of older adults and internal medicine | MSN, RN license |
MSN – DNP Leader | Focus on the basics of personnel management, policy development and implementation, budgeting, and the use of IT in advanced nursing roles. Students earn a Master’s and Doctorate | BSN/RN license |
DNP – Doctor of Nursing Practice | Readies advanced practice registered nurses as clinical experts | BSN and or MSN/RN license |
Family Nurse Practitioner Primary Care Certificate | This program allows RNs to meld their nursing skills with training in the safe, effective practice of primary care for the supervision of acute and chronic health problems of both adult and pediatric patients. | MSN/RN license |
MSN – DNP Family Nurse Practitioner | An interdisciplinary and collaborative program with a clinical component. Helps nurses learn strategic leadership in tandem with expertise in areas like rural health, public health and homeland security. | BSN/RN license |
Accelerated BSN to MSN | Provides associate’s or diploma level nurses the chance to satisfy certain core needs for an MSN program while they complete their bachelor’s degree in nursing. | RN License |
MSN – Adult Gerontology Primary Care Nurse Practitioner | Focus on acute and chronic health problems of adult patients. Clinical practice in a real world setting. | BSN/RN license |
Doctor of Nursing Practice – Family Nurse Practitioner Track (BSN to DNP) | Prepare for the highest level of nursing practice and patient centered care. Successful students earn their MSN and DNP | BSN/RN license |
Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (RN Track) | Advanced courses and training to provide care for patients with psychiatric disorders, substance abuse problems or medical organic brain disorders. | BSN/RN license |
Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) – Adult Gerontology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner (BSN Track) | Learn to provide care for seriously ill (complex acute and chronic medical conditions) for ages 13+ | BSN/RN license |
NURSE PRACTITIONER DEGREE ONLINE PROGRAMS
There are many types of nurse practitioner programs and each option has course work, a guided practicum and/or clinical experience. Some also entail a capstone or nursing project which gives you the chance to research modern issues.
If you’re earning your NP degree online, you might need to go to your campus for in person skills intensives. You may complete clinicals in local settings.
The types of courses and number of supervised practice hours depends on a nurse’s prior education. Also, what s/he chooses as a major (nursing niche).
We will start out with a brief guide that explains the different entry paths for online NP programs. We will follow this with some common NP courses. Then, take a look at some main focus areas you’ll find when you earn a NP degree online.
Often a nursing school will offer a certain program such as Family Nurse Practitioner with many path ways to pursue it. Speaking with an advisor from a grad school may lend more insight.
Five of the common entry paths for nurse practitioner programs are listed below:
- BSN to MSN: For registered nurses that enter the program with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN).
- RN to MSN: For RNs that enter the program with a hospital diploma, associate degree in nursing, or a bachelor’s degree other than a BSN. Some schools refer to this track as ADN Diploma MSN
- RN to BSN to MSN: For RNs who want the chance to earn their BSN while they work toward their MSN.
- BSN – DNP: For RNs that enter a Doctorate of Nursing Practice program with a bachelor’s degree in nursing. (also: BSN to MSN to DNP)
- MSN – DNP: For RNs with an MSN who want the chance to earn a DNP.
1
Southern New Hampshire University
- Take advantage of some of the nation’s most affordable tuition rates, while earning a degree from a private, nonprofit, NEASC accredited university
- Qualified students with 2.5 GPA and up may receive up to $20K in grants & scholarships
- Multiple term start dates throughout the year. 24/7 online classroom access.
Popular Programs
Business Administration, Psychology, Information Technology, Human Services…
2
University of Arizona Global Campus
- 99% of University of Arizona Global Campus students study online
- University of Arizona Global Campus offers affordable tuition, so college is accessible to many students.
- he University of Arizona Global Campus (formerly Ashford University) is accredited by WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC)
Available Programs
Accounting and Finance, Information Technology, Political Science…
3
Western Governors University
- Award-winning programs created to help you succeed.
- A quality education doesn’t have to be expensive. Earn an accredited degree for less.
- Programs start monthly – Apply free this week!
Sponsored Schools
WHAT ARE NP CORE COMPETENCIES?
Online nurse practitioner programs often include balanced and evidence based curricula. The aim is to help students develop ‘core competencies’ which are standards for clinical practice. Mastery of these core topics may be useful for those who are preparing to sit for national certifications after they graduate.
- Scientific Foundation – These courses aim to help students meld research, theory, and practice knowledge. You can reasonably expect to study topics such as advanced pharmacology, physiology, genetics, and communication skills.
- Leadership – These courses may help nurses learn to assume more complex roles, initiate and guide change. They may help students learn how to manage conflict, negotiate and develop their personal (ethical) leadership style.
- Quality – These courses are about quality improvement in nursing from the Quality Safety Education in Nursing (QSEN) principles and content. You might also learn about the different local, state and federal laws that govern care.
- Practice – These types of courses focus on how to identify and solve clinical problems. For instance, you might learn how to review literature and use electronic health records (EHRs). Other topics may highlight team and inter professional collaboration.
- Technology – These topics often pertain to the electronic resources nurses use to enhance patient safety. They’ll often cover the information data bases used by health care systems.
- Policy – These course topics often provide nurses with the skills to advocate for ethical policies that promote access, equity, quality, and cost. They may cover global issues like infections and population health. You may also study the regulatory process and health policy.
- Health Delivery – Many such courses focus on nurse informatics and how to use data to improve nursing practice. You might also study finance, business, billing and transitional care.
- Ethics – These courses may study ethics and how to make ethical decisions. Topics may cover things like hospices and palliative care.
- Independent Practice – These courses often discuss things like licensure, contract negotiation and regulatory issues. You might also explore different types of screenings, diagnostics and procedures. Other topics might delve into the preventative side of health care and the NP’s role in disease management.
POPULATION FOCUSES FOR NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS
Apart from core courses, NP students may choose to study a certain population group from among the following:
- Adult Gerontological
- Family (Across Lifespan)
- Neonatal, Pediatrics
- Women’s Health Gender Related
- Psychiatric Mental Health
Below you’ll find some details on common NP focuses. We suggest you contact any school that draws your attention because clinical hours and requirements vary.
Adult gerontology acute care nurse practitioner: Provides direct care for acutely and critically ill patients. Programs typically include topics such as pharmacology, health assessments, public policy in health care, and physiology.
Adult gerontology primary care nurse practitioner: Promotes holistic health care to members of the adult and older adult population through assessment, diagnosis, and holistic treatment of chronic health problems.
Executive leader: Focus on the admin side of nursing. This type of program delves into how to manage personnel, develop and implement policy, budget, and use IT.
Family nurse practitioner, primary care: Promotes holistic health care to adults and children in a family systems context. May diagnose and treat children, adults and the elderly across the lifespan. Common courses include advanced health assessment and advanced pharmacology.
Neonatal nurse practitioners: Focus on care of newborns. Students might complete extensive clinical work and niche courses. Some of these might be topics in advanced pediatric health, pharmacology, and nursing care for high risk newborns.
Pediatric nurse practitioners: Work with children from infancy through adolescence. Courses may cover pediatric primary care, child development, and psychopharmacology.
Psychiatric mental health nurse practitioners: Provide care for patients with psychiatric disorders, medical organic brain disorders, and substance abuse problems
Nurse educator: Focus on teaching to other nurses. Courses may ready grads to develop courses and programs which integrate nursing with educational philosophy.
Some common courses include:
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: Explore how to stop disease and spread good health. In this course, you may learn how to reach diverse people and help them get healthy.
Physical Exam and Health Assessment: In this course, you could learn the skills to check patients for health problems. You may study factors like age, health history, and much more.
Primary Care of Adults: Find out how to handle the health needs of adult patients at different stages of life. You could learn how to diagnose and treat many kinds of health conditions.
Advanced Pharmacology: This course may cover the role of the NP in prescribing drugs. You could learn more about drug uses, side effects, and reactions.
Health Care Information Technology: Learn how NPs use technology tools to work with data. This course may teach you how to manage records in efficient and safe ways.
Healthcare Policy, Law, and Ethics: Uncover the tough questions that may come up when working in health care. You could look at everything from legal issues to rules of conduct.
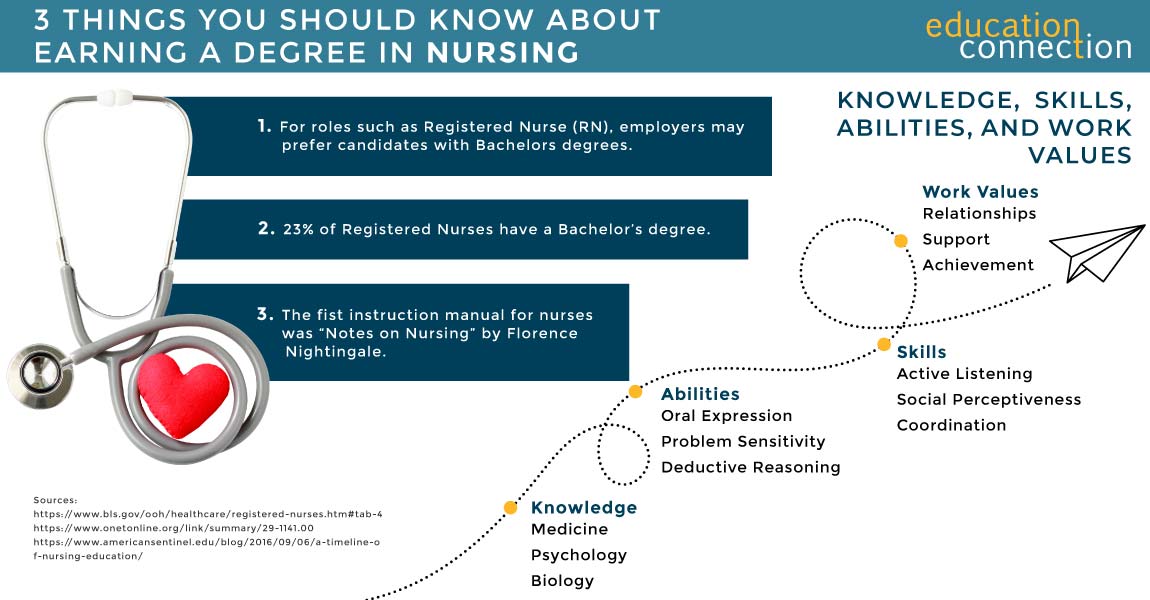
HOW LONG DO YOU HAVE TO BE IN SCHOOL TO BE A NURSE PRACTITIONER?
To become an NP, you must first complete a 4 year BSN. Post BSN, you’ll need to earn a master’s degree program that trains nurse practitioners. Called MSN or Nurse Practitioner (NP) degrees, these may take from 2 to 4 years.
Time to complete also varies with course load, full or part time format and track (see above). For instance, some who enter an MSN program with an ADN or Diploma rather than a BSN will be required to complete extra (e.g. 45 credit hours). The program often can then be completed in about 2.6 years.
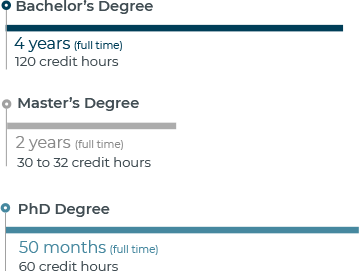
NURSE PRACTITIONER DEGREE PROGRAM EXAMPLES
| School | # of Credits Required | Start Dates | Minimum Months to Complete |
| Bradley University | 36 | Not listed | 2 years |
| Purdue Global University | 49 | multiple | 2 years |
| Walden University | 63 (quarter credits) | multiple | 27 months |
HOW MUCH DOES IT COST TO BECOME A NURSE PRACTITIONER?
The cost of an online NP program often depends on the path way. If you have fewer credits to accomplish, this may reduce overall tuition. Your tuition may depend on whether you choose an in or out of state program. Recent tuition figures for nursing practice degrees show the averages at $7,411 (in state public) and $30,100 (out of state private). In both cases, tuition is going up.
| School | # of Credits Required | Cost Per Credit | Total Tuition Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purdue Global U | 60 to 90 | $420 | $25,200+ |
| Bradley U | 36 | $850 | $30,600 |
| Walden U | 63 | $710 | $44, 730 |
TOP SCHOOLS FOR ONLINE MSN to NP PROGRAMS
According to DataUSA, 2,173 degrees awarded to students in family nursing in 2022. The majority of these programs were granted at the master’s level.
| School | 2022 Degrees Awarded | 2023/24 Tuition (Out of State unless *) |
|---|---|---|
| University of Phoenix Arizona | 224 | $9,552* |
| The University of Texas at Arlington | 141 | $29,660 |
| Excelsior College | 88 | N/A |
| Wilmington University | 79 | $12,330* |
| Indiana Wesleyan University National & Global | 71 | $8,216 |
| American Sentinel University | 167 | $10,800* |
Estimated for full time, beginning undergrad students
CHOOSING AN ACCREDITED ONLINE NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAM
Accredited online nurse practitioner programs help RNs prepare for APRN roles. If you attend an accredited online nursing school it may enable you to seek state or federal financial aid. Financial aid agencies do not fund non accredited nursing programs. But that’s not all. Grads of accredited online NP programs may also qualify to pursue advanced studies. This includes post masters certificates and PhD or DNP degrees. State licensing boards do the same as schools and look at whether or not you earned your NP degree through an accredited nursing program. Accredited online nurse practitioner programs also have to prove they meet quality standards. This means their course plan has to ready students with the core competencies.
Plus, such programs must keep their standards up – or continue to better themselves. Accreditation lasts for a certain amount of time, then a school needs to submit to review. If they want to maintain their status, it may motivate a school to stay relevant or improve. Accrediting agencies often monitor the health industry, then form policies that impact a participating schools’ syllabus.
ACEN VS CCNE
The Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education (CCNE) and the Accreditation Commission for Education in Nursing (ACEN) are two accrediting agencies. Both agencies have data bases so you can determine the status of a program or school rather than relying on the school’s website.
ACEN – Accreditation Commission for Education in Nursing (ACEN). The ACEN accredits all types of nursing education programs including master’s, bachelor’s, associate’s and diploma.
CCNE – The CCNE accredits bachelor’s, grad and residency programs in nursing. It does not accredit LPN, Diploma, or ADN programs while the ACEN does.
NURSE PRACTITIONER CAREER PATHS AND POTENTIAL SALARIES
Growth in NP roles is growing as they are in high demand and reports point to an extra 141,200 jobs through 2033.





