What is a Financial Advisor?
Before you delve into how to pursue a career a financial advisor, you should be clear on what they do.
Financial advisors are professionals who take on the responsibility of overseeing and coordinating various aspects of their client’s financial well-being. Their role extends beyond simply recommending investments or marketing financial products. They evaluate a client’s current financial situation, gain insight into their financial objectives, and develop a customized financial strategy to help them reach those objectives.
In addition to offering investment guidance, financial advisors might also assist in areas such as retirement planning, estate planning, savings, and investment management. They might also help clients reduce their taxes and maximize the returns on their financial assets.
Later in this article we provided detailed information about responsibilities, work environment, salary, and employment.
Types of Financial Advisors
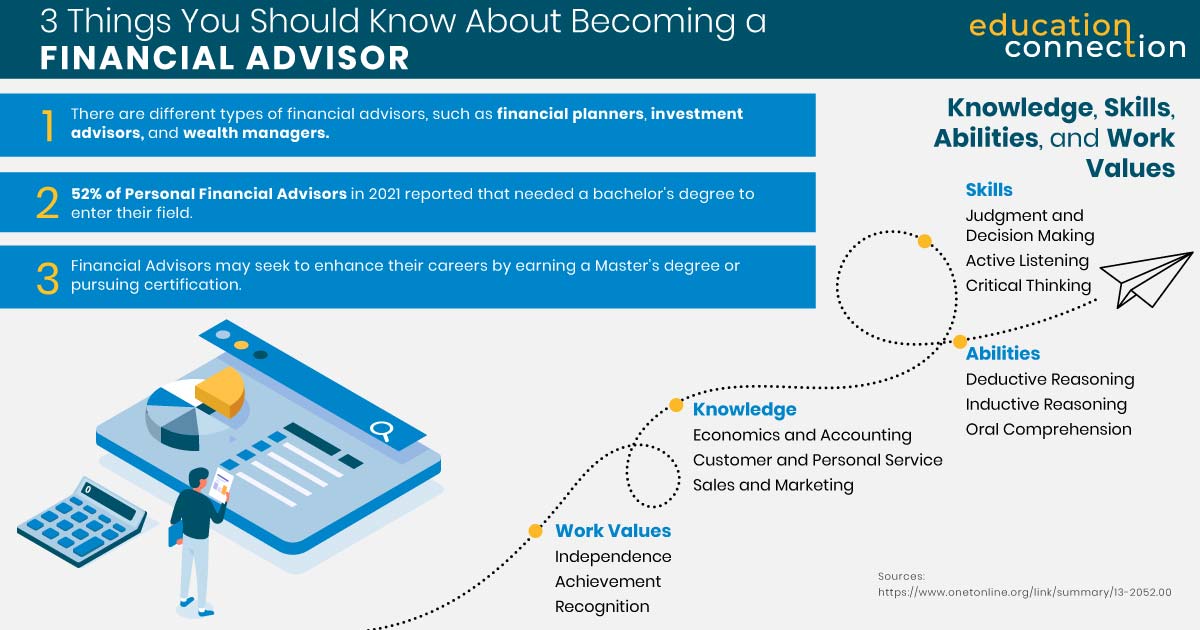
Not all financial advisors are alike with regard to their experience, knowledge, and the range of services they provide. Following are several common types of financial advisors.
Financial Planners | Wealth Managers | Investment advisors |
| Financial planners specialize in helping their clients define long-term goals—such as savings, investments, insurance, retirement, and estate planning—and creating a plan to help them achieve those goals. Many financial planners hold credentials such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)— these credentials are discussed later in this article. | Wealth managers typically work with clients who have significant wealth, often requiring a minimum investment in the millions. They provide comprehensive financial planning services along with investment advice. Their expertise extends to various aspects of their clients’ financial lives, encompassing services such as estate planning, tax assistance | These professionals help clients make informed decisions about their investment portfolios. Also known as stockbrokers, investment advisors are required to register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). |
How Do I Become a Financial Advisor?
Financial advisors usually pursue education, on-the-job training, and certification. Here’s what this path might look like:
- Education. Prospective financial advisors usually earn at least a Bachelor’s degree in an area such as finance, accounting, or economics.
- Training. Once hired, FAs often have a period of training on the job, learning skills such as how to build a network of clients and develop investment portfolios. This on-the-job training might last a year or more.
- Licenses and certifications. Personal financial advisors who engage in activities such as buying or selling stocks, bonds, or insurance policies, or providing specific investment advice, are typically required to obtain specific licenses and/or be registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Many FAs go on to pursue certification, such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP) certification, to enhance their careers.
1
Southern New Hampshire University
- Take advantage of some of the nation’s most affordable tuition rates, while earning a degree from a private, nonprofit, NEASC accredited university
- Qualified students with 2.5 GPA and up may receive up to $20K in grants & scholarships
- Multiple term start dates throughout the year. 24/7 online classroom access.
Popular Programs
Business Administration, Psychology, Information Technology, Human Services…
2
University of Arizona Global Campus
- 99% of University of Arizona Global Campus students study online
- University of Arizona Global Campus offers affordable tuition, so college is accessible to many students.
- he University of Arizona Global Campus (formerly Ashford University) is accredited by WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC)
Available Programs
Accounting and Finance, Information Technology, Political Science…
3
Western Governors University
- Award-winning programs created to help you succeed.
- A quality education doesn’t have to be expensive. Earn an accredited degree for less.
- Programs start monthly – Apply free this week!
Sponsored Schools
What Degree Should I Earn to Become a Financial Advisor?
Financial advisors typically need at least a Bachelor’s degree. There may not be any one degree employers look for—rather, a number of majors may be helpful if you’re interested in pursuing a financial advisor career path:
Today, many schools offer Bachelor’s in Financial Planning programs. These may cover subjects you need to know for the CFP (Certified Financial Planner) exam. You could study areas like estate planning, taxation, and risk management.
Some financial advisors opt to earn a Master’s degree in areas such as finance, business administration, or a related area. Earning a Master’s could help financial advisors pursue a management career path.
What Would I Study in a Financial Advisor Degree Program?
The range of topics covered in degree programs typically varies depending on degree type, major, and even school. You might focus on different aspects of business, finance, or economics. However, following are some areas that might be common in programs designed more specifically for financial advisors:
Personal Finance: Gain insights into how to plan a budget, manage money, and more. Topics covered could include taxes, credit, and making major purchases.
Money and Banking: Learn about the complex world of banking, including money, credit, treasuries, and more.
Investments: Examine how the stock market works— its risks and possible rewards—as well as types of investments and how to manage a portfolio.
Finance Regulations and Ethics: Learn the rules that govern choices about money and how to help clients reach their goals legally
How Long Does It Take to Earn a Financial Advisor Degree?
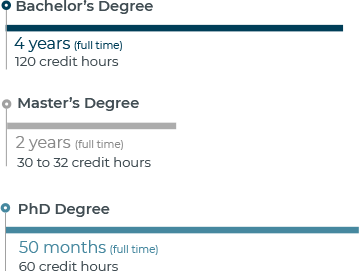
Earning a financial advisor degree, such as a Bachelor of Finance in Financial Planning, typically takes about four years of full-time study.
If you plan to earn a Master’s degree, you’ll typically need about one to two years, depending on your program and whether you study part- or full-time.
Working as a Financial Advisor
While you may have a better sense of what a financial advisor does, you might wonder what it’s like to work as a financial advisor. Read on to learn about typical responsibilities, places of work, salaries, and employment opportunities.
Financial Advisor Responsibilities
- As mentioned previously, not all financial advisors do the same thing. However, here are some common responsibilities of financial advisors as a whole:
- Meet with clients to discuss their financial goals—e.g., saving for the future, growing wealth with investments, or buying property.
- Educate clients about their options and risks
- Invest money on the client’s behalf
- Monitor clients’ money to see if their strategies need to change
Where Financial Advisors Work
Personal financial advisors typically work in offices. They might also attend conferences or conduct seminars. They may be self-employed or work for financial organizations such as banks and investment companies.
Following are the industries with the highest levels of employment for personal financial Advisors in 2022:1
| Industry | Employment | Percent of industry employment | Annual Mean Wage |
| Securities, Commodity Contracts, and Other Financial Investments and Related Activities | 191,490 | 18.00 | 164,210 |
| Credit Intermediation and Related Activities (5221 and 5223 only) | 48,360 | 2.37 | $112,700 |
| Agencies, Brokerages, and Other Insurance Related Activities | 7,560 | 0.57 | $103,860 |
| Management of Companies and Enterprises | 5,050 | 0.18 | $136,600 |
| Management, Scientific, and Technical Consulting Services | 3,470 | 0.19 | $122,240 |
Professional Certifications for Financial Advisors
Earning certification could help financial advisors stand out from the crowd. While there are many to choose from, here are three common ones to consider:
Certified Financial Planner (CFP)
The Certified Financial Planner(CFP) certification sets the benchmark for excellence in the field of financial planning. CFP professionals undergo rigorous education, training, and ethical standards to help ensure they provide quality service to clients.
To earn this CFP certification you need to earn a Bachelor’s degree, have three years of experience, agree to a code of ethics, and pass an exam. The exam tests you on key areas of financial planning such as:
- Investment and real estate planning
- Debt management
- Insurance planning
- Income taxes
- Retirement planning
- Risk management
- Employee benefits planning
- Statistical modeling
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
CFA certification is geared toward professionals who want to distinguish themselves in the area of investment management profession. To become a “Charterholder,” you must earn a Bachelor’s degree or have eligible work experience and pass an exam that covers ten knowledge areas, such as investment analysis, management, and ethics.
Personal Financial Specialist (PFS)
The Personal Financial Specialist (PFS) credential is offered to CPAs with tax and financial planning expertise. Earning a PFS helps CPAs understand the tax implications in various areas of personal financial planning. In addition to being a CPA, requirements include:
- Two years of full-time teaching or business experience in personal financial planning
- A minimum of 75 hours of personal financial planning education in the last five years
- Pass a PFP-related exam—either the PFP exams such as the Certified Financial Planner (CFP) exam
Related Career Paths
You may already have decided to pursue a career as a financial advisor, or even decided on the type of financial advisor you want to be. But if you’re not sure yet, here are some related careers that might interest you.
Sources:
1https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes132052.htm
2https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes132031.htm
3https://www.bls.gov/ooh/business-and-financial/budget-analysts.htm#tab-1
4https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes132051.htm
5https://www.bls.gov/ooh/business-and-financial/financial-analysts.htm#tab-1
6https://www.bls.gov/oes/current/oes132061.htm
7https://www.bls.gov/ooh/business-and-financial/financial-examiners.htm#tab-1
Based on national data, not school-specific information. Conditions in your area may vary. Accessed 6/30/2023.
This is an offer for educational opportunities that may lead to employment and not an offer for nor a guarantee of employment. Students should consult with a representative from the school they select to learn more about career opportunities in that field. Program outcomes vary according to each institution’s specific program curriculum.